As the demand for fast charging and power-efficient electronics accelerates across industries, USB Power Delivery (USB PD) has emerged as the universal standard. Whether you’re sourcing chargers, cables, or embedded systems for OEM/ODM production, understanding the USB PD ecosystem is now a critical advantage for buyers.
This checklist outlines everything you need to know about USB PD protocols, specifications, and component compliance as we move into 2025.
USB Power Delivery: An Overview
USB PD (Power Delivery) is a flexible charging and power negotiation protocol built into the USB-C connector. It allows devices to dynamically select charging voltage and current, delivering up to 240W under the USB PD 3.1 specification.
Key Benefits: One cable for both data and power. Negotiated power delivery based on device requirements. Supports bi-directional charging. Enables fast charging for laptops, phones, monitors, and more
Evolution of USB PD Protocols
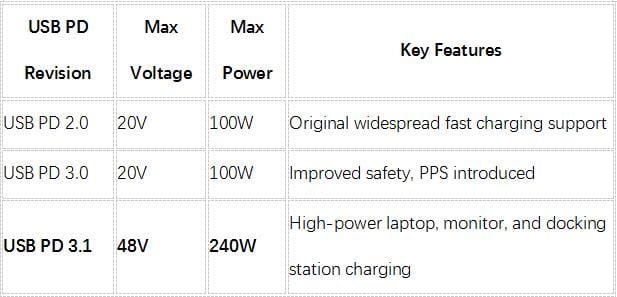
Buyer’s Tip: Always confirm if your supplier’s solution supports USB PD 3.1 with AVS (Adjustable Voltage Supply) and PPS (Programmable Power Supply) capabilities.
USB-C: The Hardware Backbone
USB PD requires the USB Type-C connector, known for: Reversible plug design. High current capacity (up to 5A). Integration with USB 3.1 and USB 4 data standards
For safety and compliance, request: E-marked USB-C cables (for >3A use). USB-IF certification for all USB cables and ports
Fast Charging & Programmable Power Supply (PPS)
Fast charging via USB PD allows smartphones and laptops to reach 50–70% charge in under 30 minutes. PPS adds further refinement with real-time voltage/current control, reducing heat and battery stress. Ideal for devices like Samsung Galaxy S/Note series, Xiaomi, and newer laptops with PPS support.
Look for: GaN Chargers with PPS. USB-C ports labeled “PD/PPS”. Support for 5V–20V adjustable output
Multi-Port & GaN USB PD Chargers
Multi-port USB PD chargers allow charging multiple devices simultaneously without compromising on speed or power. Combining PD protocols with GaN (Gallium Nitride) technology improves: Efficiency. Size reduction. Thermal management
Buyer’s Checklist: Are all USB-C ports PD-enabled? Is GaN used for better heat performance? Are ports isolated for safe multi-device charging?
Compliance Testing & Certification
For importers and OEMs, compliance ensures both performance and legal safety.
What to check: USB-IF Certification for chargers, cables, controller. Passes USB PD Compliance Test Suite (CTS). E-marked USB-C cables. Over-voltage protection and short-circuit safety
Recommended: Request compliance reports or test results before bulk orders.
B2B Sourcing Considerations for 2025
Before placing your next USB PD product order, ensure your supplier covers: PD 3.1 support up to 240W. PPS functionality for major smartphone brands. USB-IF certification for all cables. GaN chip integration for heat efficiency. Multi-port PD output. Availability of PD controllers for embedded products. USB-C cable quality (E-marked, shielded, certified). Voltage negotiation support with AVS
Final Thoughts
As USB PD becomes the global charging standard, buyers must evaluate not just wattage, but the protocols, compliance, and thermal design behind every USB-C device.
If you’re sourcing USB-C chargers, programmable power solutions, or embedded PD systems, make sure your suppliers meet the latest USB PD standards and offer proper certifications.





